In an era where digital interaction is omnipresent, human senses still play a critical role in our experience of the world. Traditional products have largely relied on sight and hearing to convey information. However, the realm of tactile feedback, or haptics, is gaining prominence and revolutionizing user interfaces in industries such as consumer electronics, Augmented Reality/Virtual Reality (AR/VR), the Internet of Things (IoT), automotive, and medicine. Haptic technology empowers engineers and designers, giving them unprecedented control to create intuitive user interfaces. This guide delves into the world of haptic feedback, highlighting electromechanical actuators, a prevalent method of stimulating our body’s vibration-sensitive mechanoreceptors.
Understanding Electromechanical Actuators
Electromechanical actuators, the core of haptic feedback, come in four main forms: Eccentric Mass Motor (ERM), Linear Resonant Actuators (LRA), Voice Coil Actuators (VCA/VCM), and Piezoelectric Actuators (PA). Each category brings unique characteristics and is suited for specific applications. From the low-frequency hum of ERM actuators to the precision and fast response of LRAs, and from the realistic haptic feel of VCAs to the efficient wide frequency range of PAs, understanding these technologies is crucial to integrating effective haptic feedback into your products.
Eccentric Mass Actuators (ERM)
ERM actuators operate on a simple but effective principle: an off-axis rotating mass, attached to a direct current (DC) motor. The frequency of the vibrations correlates to the rotational speed of the mass, offering a tactile experience that is directly influenced by the driving voltage. ERMs are especially known for their “rumble” effect, making them ideal when precise vibration patterns are not critical, but noticeable tactile feedback is sought.
These actuators are used in a variety of industrial applications, from handheld devices to heavy machinery control systems. Their simple design and ability to provide perceptible tactile feedback make them a popular choice for engineers and designers. Below, we’ll delve into the key features of ERM actuators and how they are integrated into industrial products.
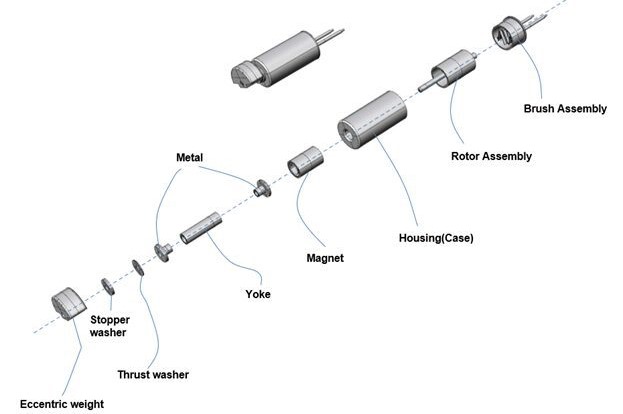
Key Features of ERM Actuators:
- Eccentric Rotating Mass: The central component of ERMs is a mass that rotates off the motor axis. This mass can be a disk or an irregularly shaped piece. As it rotates, it creates vibrations that are transmitted to the device or surface on which it is mounted.
- Adjustable Driving Voltage: The intensity of the vibrations is directly related to the voltage applied to the motor. By adjusting the voltage, engineers can control the strength and frequency of the vibrations generated by the ERM.
- Rumble Effect: ERMs are known for their ability to produce a perceptible vibration sensation. This “rumble” effect is especially useful in applications such as video games, mobile devices, and control panels, where immediate tactile feedback is desired.
- Common Applications: ERMs are used in mobile phones for call and message notifications, in smart watches for vibration alerts, in video game controllers for tactile feedback, and in medical devices for alarm signals.
Haptic feedback